Logic Circuit II (Alternative Logic Gate)
Topic: Logic Circuit II (Alternative Logic Gate)
Class: SSS Two
Definition of Alternative Logic Gates
Alternative logic gates are those that are the combination of two basic logic gates (AND, OR, NOT). They are called derived gates or universal gates because they combine the function of basic gates into a single component.
Universal Gates: NAND and NOR
NAND and NOR gates are known as Universal Gates because any other logic gate (AND, OR, NOT) can be constructed entirely using only one type of these gates. This property simplifies circuit manufacturing.
NAND Gate
The NAND gate (NOT-AND) is the combination of an AND gate followed by a NOT gate. Its output is LOW (0) only when all of its inputs are HIGH (1).
Logic Symbol for the NAND Gate

Or

Truth Table for NAND Gate
| Input A | Input B | Output C |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NAND Gate Equation
For a two-input NAND gate, the Boolean equation is:
$X = \overline{A \cdot B}$
This means “X equals A AND B NOT.”
NOR Gate
The NOR gate (NOT-OR) is the combination of an OR gate followed by a NOT gate. Its output is HIGH (1) only when both inputs are LOW (0).
Logic Symbol for the NOR Gate

or

Truth Table for NOR Gate
| Input A | Input B | Output C |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NOR Gate Equation
For a two-input NOR gate, the Boolean equation is:
$X = \overline{A + B}$
This means “X equals A OR B NOT.”
XOR (Exclusive-OR) Gate
The XOR gate acts as an inequality detector. The output is HIGH (1) if the inputs are different, but LOW (0) if they are the same.
Logic Symbol for the XOR Gate
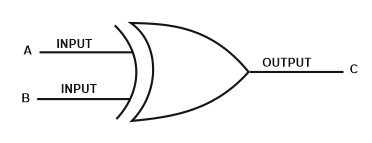
Truth Table for XOR Gate
| Input A | Input B | Output C |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
XOR Equation and Application
$X = A \oplus B$
Or equivalently:
$X = A\overline{B} + \overline{A}B$
The XOR gate is a key component in digital arithmetic circuits such as adders.
XNOR (Exclusive-NOR) Gate
The XNOR gate is the inverse of the XOR gate. It acts as an equality detector. The output is HIGH (1) only when the inputs are the same (equal).
Logic Symbol for the XNOR Gate

Truth Table for XNOR Gate
| Input A | Input B | Output C |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
XNOR Equation and Application
$$X = \overline{A \oplus B}$$
$$X = AB + \overline{A}\,\overline{B}$$
The XNOR gate is primarily used as an equality comparator and in parity checking circuits.
Uses of Logic Gates 💡
Logic gates are used to design:
:- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Built entirely of logic gates (especially XOR) to perform addition, subtraction, and comparison.
- Data Storage: Gates are wired together to create memory cells (flip-flops, latches).
- Multiplexers/Demultiplexers: Used to route signals within computers and communication systems.
- Safety Systems: AND/NAND gates ensure multiple safety conditions are met before operation.
- Traffic Controllers: Logic circuits sequence traffic lights using timing and sensors.
🧠 Test Your Knowledge
1. Which of the following is formed by combining an AND gate and a NOT gate?
OR gateXOR gate
NAND gate
NOR gate
2. What will be the output of a NOR gate when both inputs are 0?
01
2
None of the above
3. The Boolean expression for a NAND gate with inputs A and B is:
$A + B$$AB$
$\overline{A \cdot B}$
$\overline{A} + \overline{B}$
4. Which gate is often called an equality detector?
XOR gateXNOR gate
OR gate
NAND gate
5. Which gate is considered a "Universal Gate"?
ANDXOR
NOR
NOT
Great information
ReplyDeleteThis as being a good job
ReplyDeletethanks niggas
ReplyDeleteTHX A LOT YALL NIGGAS
DeleteSUPPP NIGGAAA
ReplyDelete