Basic Computer Operations
Class: SSS One
Definition of Booting
1. Booting is defined as the processing of starting the computer.
2. Booting can also be defined as the initial set of operations that the computer performs when power is switched on.
Description of the Booting Process
When the computer’s power is first turned on, the CPU initializes itself and looks for the system's UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) or BIOS (Basic Input Output System). The UEFI or BIOS is the first program that runs. It performs the Power-On Self-Test (POST), which begins by checking the firmware itself and then proceeds to initialize and test critical hardware components such as the CPU, memory (RAM), graphics card, and basic input/output devices.
The UEFI or BIOS then consults its configuration settings to determine the boot order. This order specifies which devices the firmware should check for a bootable operating system. Once a bootable device is found (e.g., a hard drive, SSD, USB drive), the UEFI firmware loads a small program called the bootloader from that device.
The bootloader then takes over, loading the operating system kernel into memory and starting the OS. For a computer to successfully boot, its UEFI firmware, bootloader, operating system, and essential hardware components must all be functioning correctly. Failure in any of these areas can lead to a failed boot sequence.
Types of Booting
- Cold booting
- Warm booting
Cold booting is also known as Hard booting. This is the process of turning the computer system ON by pressing the power of the system unit and the monitor.
Warm booting is also known as Soft booting. This is the process when the operating system alone is restarted (without being switched off) after a system crash or freeze. On PCs, warm booting is done by pressing the Control, Alt, and Delete keys simultaneously.
Both types of booting clear out (for the time being) the bugs, bombs, memory conflicts, and other idiosyncrasies (peculiarities) of the operating system.
Cold Booting vs Warm Booting
Difference between Cold Booting and Warm Booting
| Cold Booting | Warm Booting |
|---|---|
| Use of power-switch is involved | It involves shortcut keys e.g (CTRL+ALT+DEL) or software commands |
| It is done when the system is already OFF | It is done when the system is ON |
| CPU stops working | CPU undergoes a reset but doesn't lose power |
| Memory and BIOS/UEFI are fully reset and re-initialized | Memory is largely flushed, and BIOS/UEFI is not fully re-initialized |
| The computer may not necessarily have a program error before it is performed (e.g., initial startup, after hardware installation) | It is often necessary when a program encounters an error or to restart the OS for updates or other reasons without a full power cycle |
| Generally takes longer to complete due to full hardware initialization. | Generally faster as it skips some hardware checks. |
| Ensures all system resources are completely reset, potentially resolving deeper issues. | May not resolve issues that require a full power cycle and hardware re-initialization. |
Windows Desktop
Windows desktop is the graphical user interface (GUI) of the Windows Operating System. The desktop is what is displayed when you log in on most operating systems. It provides a platform for the user to interface with or operate the computer by pointing and clicking the mouse button on graphical symbols to send data and instructions to the computer and get out of it.
NOTE: There is a difference between Window and Windows in computer. Whenever a program is started in windows it occupies a certain space on the screen in which it runs. That frame or box is called a window. While windows is an Operating System (OS) from Microsoft Corporation.
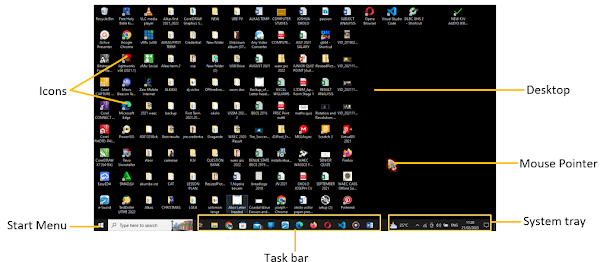
Elements of Windows Desktop
a. Mouse pointer: The mouse pointer indicates the current position of the mouse
b. Icons: Icons are the shortcut to folders, files programs and other items
c. Desktop: The launch pad for application and workspace
d. Taskbar: The taskbar is located at the bottom of the screen.
Components of the Taskbar
i. Start menu: Gives quick access to computer settings and computer programs
ii. Quick launch Toolbar: The quick launch toolbar is a section of your taskbar near the Start menu where you can add shortcuts to programs. The Quick Launch toolbar always stays visible, even when you have a window open, for easy access to your shortcuts.
iii. System tray: The system tray is a notification area on the operating system taskbar.
Running an Application Program
- Click the Start button.
- Select All Programs or All Apps.
- Navigate and click the intended program.
- If the icon is on the desktop, double-click it.
Shutting Down Windows
Method I
- Close all running applications.
- Select Start > Turn Off Computer.
- Click Turn Off.
Method II
- Close all applications.
- Press Alt + F4.
- Select Shutdown.
Method III
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete.
- Click the power icon.
- Choose Shut down, Restart, or Sleep.
amazing work
ReplyDeleteWow....This is great
ReplyDeleteNice one
Deletebravo
ReplyDeleteThis blogger is amazingly wonderful!
ReplyDeleteGod will bless the work of your hand.
Amen
DeleteThanks alot, is very helpful.
ReplyDeleteThis are lovely and well detailed. Well done ✅👍
ReplyDeleteThanks for your kind words. You're always welcome
DeleteWow this is a nice work keep it on
ReplyDeleteThis is a stunning work well done
ReplyDeleteThanks for your kind words.
DeleteThank you so much for your amazing work. They are so helpful and stress free in accessing. 👍💯
ReplyDeleteThanks for your kind words.
DeleteLove 💕 your work,easy to get ❤️
Deletehow fa
ReplyDelete